From Exclusive to Inclusive Remembrance: The Civilian War Memorial
Librarian Lim Tin Seng shares the story of the Civilian War Memorial that commemorates casualties of the Japanese Occupation – and how its symbolism has evolved from inception to the present day.

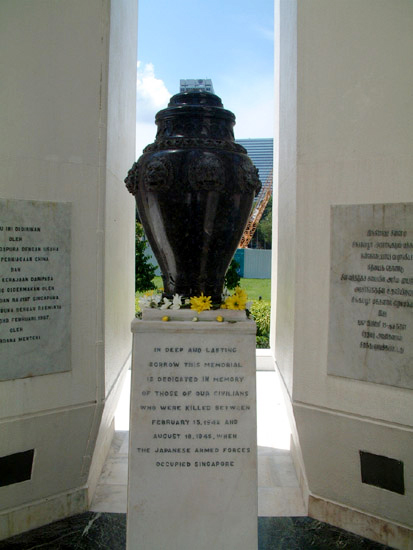
The Civilian War Memorial is a monument that commemorates those who lost their lives during the Japanese Occupation of Singapore (February 1942–September 1945). Situated in a park near the busy junction of Bras Basah Road and Beach Road in downtown Singapore, four 64.7-metre-tall obelisks were erected in the middle of a shallow pool. The merging at their bases symbolises the collective suffering of four ethnic groups in Singapore – the Chinese, Malays, Indians and Eurasians – during the Japanese Occupation.
Its is interesting to note that the Civilian War Memorial that stands today is very different from what would have resulted if the proposed original design had been adhered to. The campaign for a war memorial was initiated by the Chinese community and intended to commemorate specifically the victims of the Sook Ching massacre, who had been predominantly Chinese.
However, when the government took over the campaign, the memorial was “moulded to the cause of nation building”.1 It was reshaped into one that enshines “a national ideology of Singapore being united through having undergone [a] common suffering”.2
The Sook Ching Massacre
Sook Ching was a two-week mass screening operation carried out by the Japanese military on 18 February 1942 – three days after the fall of Singapore – to purge anti-Japanese elements within the Chinese community. In order to identify supposed anti-Japanese Chinese, the military summoned all Chinese males between the ages of 18 and 50 to designated screening centres. Those who passed the inspection were issued “good citizen” cards, while those who failed were detained, sent to remote locations across Singapore, and executed.3
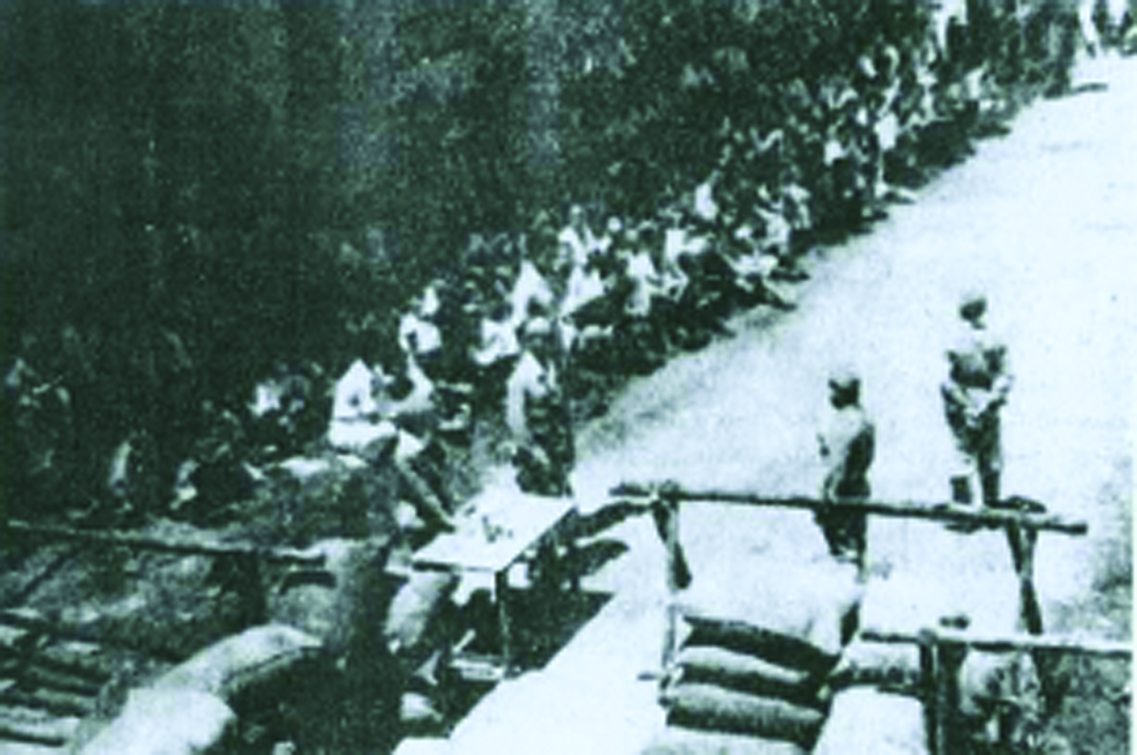
The Japanese had various methods for executing the Chinese suspected of being anti-Japanese. The first method was carried out off the shores of Tanjong Pagar, Punggol Beach and Tanah Merah Besar Beach. The Japanese first sent the suspects out into the sea in boats. Then with their hands and legs tied together, these suspects were thrown overboard before being machine-gunned to death.4

The second method was carried out in remote areas of Singapore such as Bedok and Siglap. The Japanese first forced the suspects, herded with ropes, to march deep into the jungle before ordering them to dig large ditches. They were then instructed to line up at the edges of these ditches and machine-gunned to death.5
The third method of killing took place on the beaches of Changi. The suspects transported to this site were first ordered to march to the shore. With their backs to the firing squad, they were mowed down with machine-gun fire.6
This ordeal was recounted by Chan Cheng Yean, a survivor of a Bedok execution on 28 February 1942:
Yap Van Hong, another Sook Ching survivor of a Changi beach massacre, narrated his experience:
The total number of Chinese killed during the Sook Ching operation varies considerably according to different reports. The Japanese put the figure at about 5,000, while the Chinese estimated it to be around 100,000. But it has been widely assumed that the number of victims was between 25,000 and 50,000.7 Furthermore, after the operation, the Chinese community had to raise $50 million as “tribute money” to pay the Japanese so as to prove their loyalty.8

After the Japanese Occupation, the Chinese community tried to seek closure. Organisations such as the Singapore Chinese Massacred Appeal Committee and Tan Kah Kee’s fundraising committees, namely the China Relief Fund Committee of Singapore and the South Seas China Relief Fund Union, were among the first to attempt to determine the number of Chinese killed during the Sook Ching operation as part of the effort to press the Japanese government for monetary compensation.9 They also proposed the construction of a war memorial for Sook Ching victims. Despite having reported that they had secured a site for the memorial, the plan failed to materialise. A widely cited reason for the lack of progress was the inability to locate the massacre sites In order to rebury the dead at the memorial site.10
The failure to formally set up a memorial site, however, did not stop the relatives of Sook Ching victims from carrying out their own mourning rituals. Driven by the anxiety to appease the souls of their loved ones who had died violently and without a proper burial, families set up ancestral tablets for the victims in their homes so that they could make the proper offerings to their dead. This was the least the families could do to prevent the dead from becoming “hungry ghosts”.11
Chinese academia In Singapore also devised their own way of commemorating Sook Ching victims by collecting and publishing the names of the victims. Although this effort began in late 1945, it was not until 1955 that a “most fully recorded” name list was published by Hsu Yun-Tsiao in the Journal of the South Seas Society. The list had about 7,100 names and included the names of victims from Singapore and Malaya.12
A Sook Ching Memorial
In February 1962, a Sook Ching mass grave was unearthed by sand-washing workers in Siglap.13 This discovery reawakened the painful collective memories of the Chinese in Singapore and triggered a strong reaction from the community.14
Among the first to respond was the Singapore Chinese Chamber of Commerce (SCCC). It dispatched a team to inspect the Siglap site and to locate other mass graves. When the team returned with further discoveries in Bedok, Bukit Timah, Changi, East Coast and Yio Chu Kang, the SCCC set up an action committee on 1 March 1963 to manage the exhumation of the mass graves. The committee also initiated a campaign to erect a memorial. This was to provide a final resting place for the Sook Ching victims and a site for their families to carry out mourning rituals.15 To “avenge” the Sook Ching victims, the SCCC demanded that the Japanese government compensate the Chinese community for the atrocities committed against them, a gesture that the SCCC referred to as a “blood debt”.16
The SCCC’s demands, however, were refused by the Japanese government. Through its consulate in Singapore, the Japanese government issued a statement that compensation claims had already been settled in the ratification of the San Francisco Treaty in 1951. They added that furthermore they had no reason to address the matter as the Singapore government had not lodged any such demand.17
The Japanese government’s response was swiftly rebutted by Ko Teck Kin, then president of the SCCC. Speaking to the press on 3 March 1962, Ko reiterated that the SCCC’s demand was “just and reasonable”. He then berated the Japanese government, saying that it was using the San Francisco Treaty “as an excuse not to address the problem”. Ko further added that the massacre carried out by the Japanese military was “a crime that has nothing to do with the treaty”. He also said the treaty did not give any justice to the families because it did not “give even a single cent” to them.18
In the weeks that followed, the press published many reports on the new discoveries of mass graves and the ongoing exhumation process. These were accompanied by comments expressing the frustration over the fact that even 20 years after the Japanese Occupation, the Chinese community was still searching for the closure they needed.19 The press also urged the Singapore government to “unconditionally offer its assistance” to help the SCCC’s action committee erect a memorial so that “the step of appeasing the dead and consoling the victims’ relatives could be carried out more smoothly”.20
The Singapore government, however, did not favour the perception of the proposed memorial being dedicated to the Chinese community alone because they felt that the nation suffered collectively during the Japanese Occupation.21 On 14 March 1962, then Prime Minister Lee Kuan Yew raised this issue before the Legislative Assembly. He said that it was “difficult” for the government to confirm the “actual Identity of the persons who had been massacred”, only that it was certain that the “people of Singapore as a whole” had “suffered by these massacres”. As a result, the government felt that any “atonement should be made to the people of Singapore collectively”.22
An Inclusive Memorial
On the insistence of the government, the SCCC began to pursue the campaign with a new multiethnic dimension. On 25 July 1962, the SCCC agreed that any compensation from the Japanese government would not be paid to relatives of Sook Ching victims but to the government, who would spend it with the interests of the nation in mind. On 15 March 1963, after the government allocated the present site on which the SCCC could erect a memorial, the SCCC in turn announced that it would work with the government to build a memorial for all victims of the Japanese Occupation, regardless of ethnicity. The announcement also came with the decision that the SCCC and the government would not rebury the excavated remains in a common grave as had been planned earlier. Instead, these remains would be cremated and placed at the proposed memorial site. This was decided in order to accommodate burial practices of all the ethnic groups.23
On 9 April 1963, the SCCC added representatives from other ethnic groups to its action committee for the war memorial campaign. A.H. Allwie and Ja’afar Shahid were appointed to represent the Malay community, while the Indian community was represented by D.T. Assomull and P.T. Nathan. The representative for the Eurasian community was Theo Leijssus.24
To realise the memorial, the government agreed to cover half of its construction cost, which was estimated to be about $500,000. The government also facilitated the SCCC’s raising of the other half of the costs by allowing them to solicit public donations.25 Lee also personally supported the SCCC’s fundraising activities by attending one of its donation drives on 21 April 1963, where he made a donation of $100. He also took the occasion to remind the people that the process of mourning the victims of the Japanese Occupation was also about remembering the hardship that the people of Singapore had endured. He said that the government “could have built this memorial without public contributions”, but decided “that the memorial will have more meaning and give more satisfaction to the thousands of people who have been so deeply hurt during the Japanese occupation if the people themselves contribute towards the memorial”.26 Lee repeated this message in his speech at the “Breaking the Sod” ceremony for the memorial on 15 June 1963.
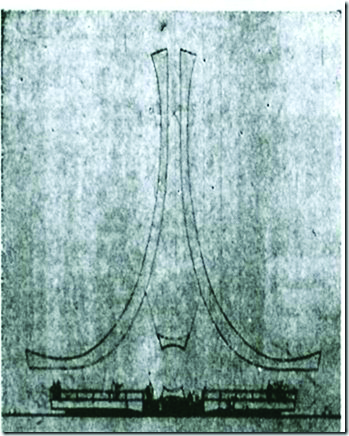
The government also played a part in the design of the memorial. After the site for the memorial was announced, architecture firm Swan and Maclaren was commissioned to design it. The design that was unveiled on 31 May 1963 featured two inverse arches rising to a point with a total of 12 water fountains at the front. It did not contain any of the multiethnic characteristics that we see in today’s memorial.27 In September 1965, the government requested changes to the design. Swan and Maclaren was again commissioned to produce a new design.28 This resulted in the memorial that we see today.
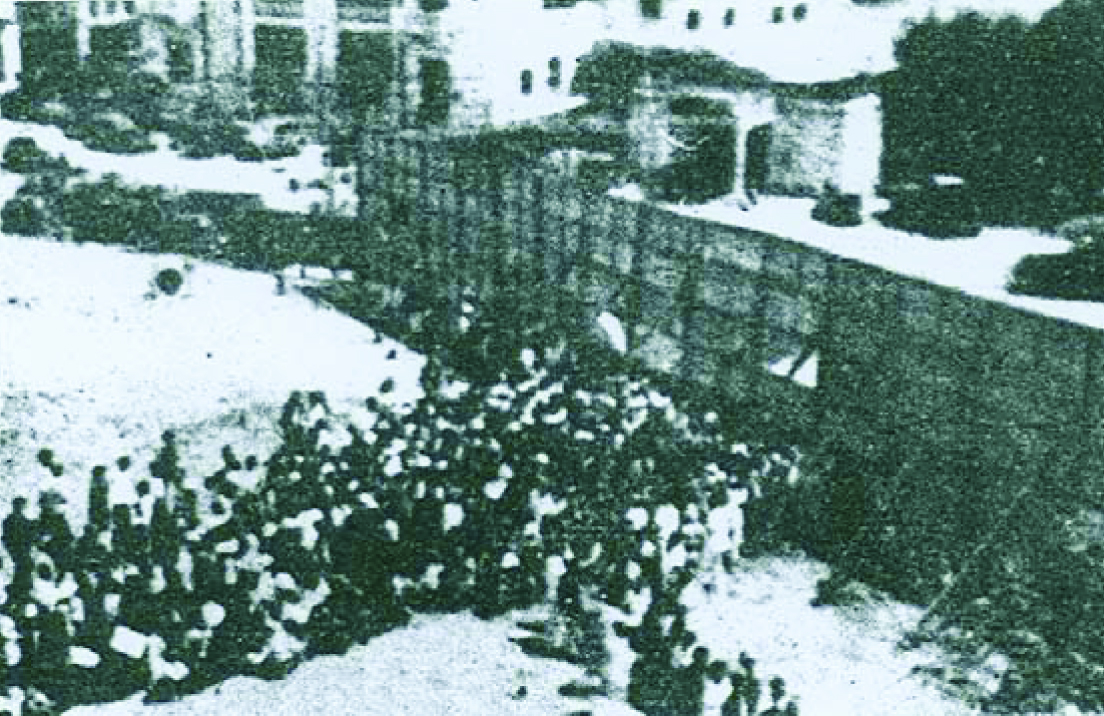
Besides overseeing the building process, the government also worked with the Japanese government to resolve the matter of compensation. An agreement was reached on 25 October 1966: the Japanese government agreed to pay a total of $50 million to the Singapore government.29 By then, the SCCC and the government had completed the exhumation of the mass graves. The remains that were exhumed from more than 50 mass graves were stored in 606 urns.30 Before they were buried on 1 November 1966, the public was invited to pay their last respects from 28 to 31 October 1966.31

On 1 November 1966, a ceremony was held to observe the interment of the 606 urns. The urns were buried on both sides of the memorial podium.32 At the end of the reburial, Soon Peng Yam, then president of the SCCC, laid a wreath at the memorial “on behalf of the Singapore people” before leading public mourners, other members of the SCCC and the action committee for the war memorial campaign to observe a three-minute silence.33 During the ceremony, an SCCC official extended an invitation to all religious representatives for the unveiling ceremony of the memorial the following year.34
The Civilian War Memorial was unveiled on 15 February 1967, 25 years after the fall of Singapore. The unveiling ceremony was attended by thousands of mourners from the public as well as leaders of the Inter-Religious Council comprising representatives from the Islamic, Buddhist, Christian, Hindu, Jewish, Sikh and Zoroastrian faiths.35
During the ceremony, Prime Minister Lee unveiled a plaque and laid the first wreath at the foot of memorial, before joining guests and the crowd in a three-minute silence. He then highlighted the symbolism of the memorial in his speech:
Conclusion
The government reshaped the Civilian War Memorial from one that was intended to commemorate Sook Ching victims and the Chinese community to a memorial that honoured all victims of the atrocities during the Japanese Occupation, regardless of ethnicity.
On 15 February every year, a commemorative service held at the site illustrates what the Civilian War Memorial now symbolises. The service is led by members of the government and the SCCC (later renamed Singapore Chinese Chamber of Commerce and Industry). It is attended by members of the public and representatives of religious groups, business and clan associations, and schools. Former prisoners-of-war from Britain, New Zealand and Australia, as well as veterans of the battles of Singapore and Malaya, are also frequently present.
During the service, the SCCC president lays a wreath at the foot of the memorial before leading the attendees in prayer and in observing a minute of silence. The memorial has shed its original motivations as an exclusive emblem of remembrance to now become a monumental reminder of the government’s vision of a multiethnic society.
The author wishes to acknowledge the contributions of Dr Ernest C.T. Chew, Visiting Professorial Fellow, Institute of Southeast Asian Studies, in reviewing this article.

Librarian
Lee Kong Chian Reference Library
National Library
REFERENCES
Akashi, Y. (1970, September). Japanese policy towards the Malayan Chinese, 1941–1945. Journal of Southeast Asian Studies, 1 (2), 61–89. Retrieved from JSTOR via NLB’s eResources website.
Blackburn, K. (2000, December). The collective memory of the Sook Ching massacre and the creation of the Civilian War Memorial of Singapore. Journal of the Malaysian Branch of the Royal Asiatic Society, 73 (2) (279), 71–90. Retrieved from JSTOR via NLB’s eResources website.
Chew, D., & Lim, I. (Eds.). (1992). Sook Ching. Singapore: Oral History Department. (Call no.: RSING 959.57023 SOO)
Fusamaya, T. (1997). Memoir of Takao Fusamaya: A Japanese soldier in Malaya & Sumatra. Bangi: Penerbit Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia. (Call no.: RSING 940.5148152 FUS)
Hsu, T. (1955). Introduction of the record of Malayan Chinese victims during the Japanese Occupation. Journal of the South Seas Society, 11 (1), 1–220.
Knauer, L.M., & Walkowitz, D.J. (Eds.). (2004). Introduction (pp. 1–17). In Memory and the impact of political transformation in public space. Durham, N.C.: Duke University Press. (Call no.: RART 720.103 MEM)
Lim, P. (2000). War and ambivalence, monuments and memorials in Johor. In P.P.H. Lim & D. Wong (Eds.), War and memory in Malaysia and Singapore. Singapore: Institute of Southeast Asian Studies. (Call no.: RSING 959.503 WAR)
Luo, Y.H. (Ed.). (1986). Singapore Chinese Chamber of Commerce & Industry 80th anniversary souvenir. Singapore: Chen Qi You. (Call no.: Chinese RSING 380.10655957 SIN)
Modder, R. (2004). The Singapore Chinese Massacre, 18 February to 4 March 1942. Singapore: Horizon Books. (Call no.: RSING 940.5405095957 MOD)
Ward, A.H.C. et al (Eds.). (1994). The memoirs of Tan Kah-Kee. Singapore: Singapore University Press. (Call no.: RSING 338.04092 TAN)
Zhang, L. (Ed.). (2004). Survey of the Chinese victims in Malaya and Singapore under Japanese occupation. Nanjing: Jiangsu ren min chu ban she. (Call no.: Chinese RSING 940.5425 SUR)
NOTES
-
Blackburn, K. (December 2000). The Collective Memory of the Sook Ching Massacre and the Creation of the Civilian War Memorial of Singapore. Journal of the Malaysian Branch of the Royal Asiatic Society, 73(279), 73. ↩
-
Blackburn, Dec 2000, p. 88. ↩
-
Fusayama, Takao. (1997). Memoir of Takao Fusayama: A Japanese soldier in Malaya & Sumatra. Bangi, Selangor: Penerbit Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, p. 101. ↩
-
PRO: WO 235/1004, Defendants : Nishimura Takoma, Kawamura Saburo, Oishi Masayuki, Yokota Yoshitaka, Jyo Tomotatsu, Onishi Satoru, Hisahatsu Haruji. ↩
-
PRO: WO 235/1004. ↩
-
PRO: WO 235/1004. ↩
-
Blackburn, Dec 2000, p. 75. ↩
-
Blackburn, Dec 2000, p. 74. ↩
-
Ward, A.H.C. et al (Eds.). (1994). The memoirs of Tan Kah-Kee. Singapore: Singapore University Press, pp. 444–446. ↩
-
Blackburn, Dec 2000, p. 77. ↩
-
See Hsu Yun-Tsiao. (June 1955). “Introduction of the record of Malayan Chinese victims during the Japanese Occupation,” Journal of the South Seas Society, 11, Part 1, pp. 1–220. ↩
-
Mass war graves found in Siglap’s ‘valley of death’. (1962, February 24). The Straits Times, p. 4. ↩
-
Blackburn, Dec 2000, p. 82. ↩
-
War massacre of civilians: Compensation demand. (1962, March 1). The Straits Times, p. 18. ↩
-
Sin Chew Jit Poh, 1 Mar 1962. ↩
-
Blackburn, Dec 2000, p. 82. ↩
-
Sin Chew Jit Poh, 3 Mar 1962. ↩
-
Sin Chew Jit Poh, 3 Mar 1962. ↩
-
Sin Chew Jit Poh, 3 Mar 1962. ↩
-
Blackburn, Dec 2000, p. 84. ↩
-
Government policy on “Mass Graves” of People Massacred by Japanese. Singapore Legislative Assembly Debates: Official Report. 3rd session of the first legislative assembly, part IV, Vol. 18, 14 March 1962, pp. 12–14. ↩
-
Sin Chew Jit Poh, 14 Mar 1963. ↩
-
Sin Chew Jit Poh, 6 Apr 1963. ↩
-
Nanyang Siang Pau, 29 Mar 1963. ↩
-
English version of a Text Speech by the Prime Minister, Mr Lee Kuan Yew, at a Meeting of the Memorial Fund Committee at the Victoria Theatre on Sunday, 21 April 1963 at 10 a.m., in Prime Minister’s speeches, interviews, statements, etc., Singapore: Prime Minister’s Office, 1959–1980. ↩
-
Sin Chew Jit Poh, 31 May 1963. ↩
-
Luo, Y.H. (Ed.). (1986). Singapore Chinese Chamber of Commerce & Industry 80th anniversary souvenir. Singapore: Chen Qi You, 339. ↩
-
Shiina flies in for a two day good-will visit. (1966, October 25). The Straits Times, p. 4. ↩
-
Blackburn, Dec 2000, p. 81. ↩
-
Memorial re-burial of wartime victims of Japs. (1966, October 24). The Straits Times, p. 9. ↩
-
Lim, B.T. (1966, November 2). Remains of massacre victims laid to rest. The Straits Times, p. 11. ↩
-
War memorial is unveiled. (1967, February 16). The Straits Times, p. 17. ↩

